Introduction:
In order to provide patients with safe and effective treatments worldwide, pharmaceutical manufacturing is essential. There are several stages to the process, from research and development through production and quality control, and it is intricate and strictly regulated. This blog will examine important facets of pharmaceutical manufacture, illuminating the rigorous guidelines, technological advancements, and quality assurance procedures that guarantee the creation of safe and effective medicines.
- Regulatory Standards:
The production of pharmaceuticals is subject to stringent regulatory frameworks that are upheld by health agencies like the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These organisations create policies and rules to guarantee the security, effectiveness, and calibre of pharmaceutical items. The importance of adhering to strict controls and Good Manufacturing Practises (GMP) is paramount.
- Research and Development (R&D):
It takes a lot of research and development to find prospective therapeutic candidates before a medication can be created. This calls for a multidisciplinary strategy that integrates preclinical research, medicinal chemistry, and pharmacology. Clinical trials are one stage of development where promising substances go through where their safety and efficacy are thoroughly assessed.
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) Production:
The essential therapeutic elements of drugs are their APIs. Pharmaceutical producers are required to follow stringent quality standards and ensure the accurate synthesis or extraction of APIs. To verify the API’s authenticity, purity, and potency, this calls for rigorous quality control procedures. Accurate characterisation relies on the use of cutting-edge analytical methods like mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
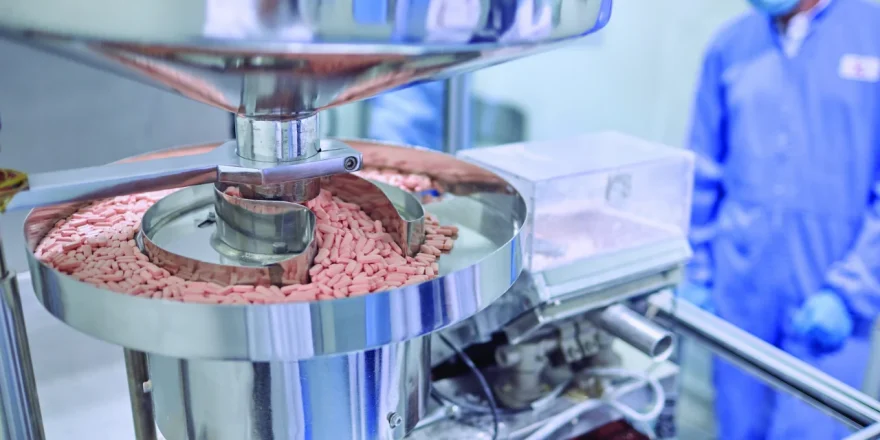
- Formulation Development:
The process of developing a final dosage form, such as tablets, capsules, or injections, that safely and effectively delivers the API to the patient is known as formulation development. At this stage, scientists take into account elements including bioavailability, stability, and patient acceptability. To ensure consistent medication release, suitable dissolution rates, and suitable shelf life, formulations are put through extensive testing.
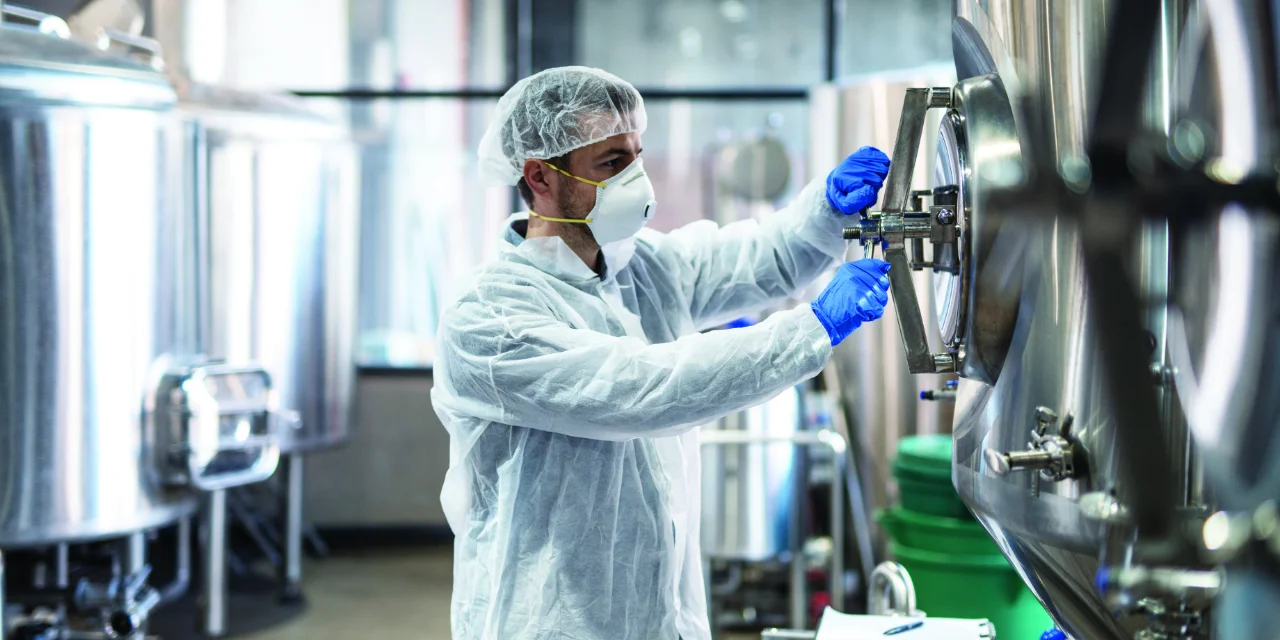
- Manufacturing Processes:
To turn API and excipients into completed dosage forms, pharmaceutical manufacturing processes like blending, granulation, compression, and coating are used. Modern manufacturing equipment and facilities are used to ensure exact control over crucial process parameters, maintain hygiene, and prevent cross-contamination. Systems with automation and computers operate more effectively and can be tracked.

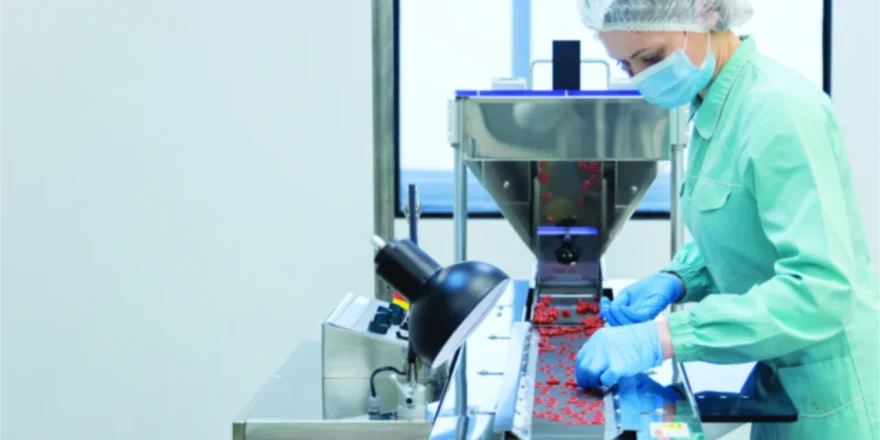
- Quality Control:
Throughout the entire manufacturing process, strict quality control methods are crucial. Samples are frequently taken and examined to ensure that the product complies with the requirements. Advanced analytical techniques are used in quality control laboratories to evaluate things like impurity profiles, dissolving rates, and content uniformity. To protect the integrity of the product, any deviations are rigorously investigated and corrected.
- Packaging and Labeling:
In order to guarantee the safe and precise administration of pharmaceuticals, proper packaging and labelling are essential. Regulations controlling packaging components, child-resistant closures, and tamper-evident elements must be followed by pharmaceutical makers. Healthcare professionals and patients need accurate labelling to provide information on dosing guidelines, storage requirements, and potential side effects.
Conclusion:
The production of pharmaceuticals is a complex, tightly controlled process that maintains the quality and security of pharmaceutical products. Every stage is carried out with extreme care, including formulation, manufacture, and quality control. To guarantee the accessibility of dependable and high-quality pharmaceutical products for patients around the world, regulatory compliance and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practises are crucial. We may appreciate the group efforts that contribute to the wellbeing and health of people around the world by understanding the intricacies and strict requirements of pharmaceutical manufacture.